

| Wrist Arthroscopy | |
|---|---|
 |
Top of page
Procedure
Before surgery can be started, the patient has to be positioned in such a way that the wrist is stabilized. In order to do this, the patient has to be placed on the operating table with his or her face upward. The wrist of the arm on which will be operated on, has to be placed on a separate operating table on the side of the other operating table. To properly stabilize the wrist, the patient's elbow is flexed and the forearm is immobilized by using a traction apparatus. By using a traction apparatus, it will also become easier to insert the instruments.
Techniques
In recent years, wrist arthroscopy is becoming a more familiar technique for the diagnosis and treatment of various wrist abnormalities. Every surgeon has his or her own preference, concerning the variety of available techniques. In this subsection, not all techniques will be described. A description of the most commonly used techniques will be given.
Before surgery
To prevent postoperative infections, the amount of pathogens in the operating-room has to be minimized. In order to achieve this, the surgeon, assistants, equipment and the operation area have to be sterile during the operation. Furthermore, the doors in the operating-room should not be opened, or this should at least be limited. Before the patient can undergo wrist arthroscopy, he or she has to be positioned in a specific way. This operation procedure has already been thoroughly described earlier in subsection ‘’Procedure’’. The patient will only be operated on when every requirement for surgery is implemented.
Entrance
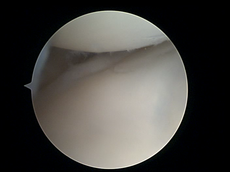
To perform wrist arthroscopy, the instruments will have to be inserted in the wrist. The surgeon will start by making a small incision for creating a so-called portal. After the incision has been made, the portal is used to insert a scope. This scope will provide the visualization. In that way, the surgeon will be able to orient within the joint of the wrist. Once a clear view of the wrist is obtained, a possible problem can be identified. This problem, for example a TFCC lesion, may then immediately be solved by operative treatment.
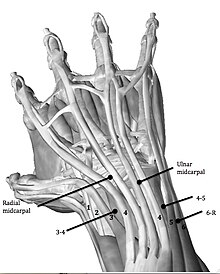
Midcarpal Ulnar portal (MCU)
- Allows visualization of the lunocapitate(LC), lunotriquetral(LT) and triquetrohamate (TH)joints.
Dorsal Distal Radioulnar joint portal (DDRUJ)
- Both the proximal and distal DRUJ can be used.
- It’s the best way to get a clear view of the DRUJ
Volar Distal Radioulnar joint portal (VDRUJ)
- Used for assessing the TFCC attachment
Top of page
Diagnostic Indication
Persistent pain in the wrist after conservative treatment is the major indication for a diagnostic wrist arthroscopy. Conservative treatment consists of wrist immobilization, oral NSAIDs and/or injection with corticoids. Diagnostic wrist arthroscopy may also be indicated when other imaging techniques, such as MRI and ultrasonography, need confirmation on observed uncertainties or when other imaging techniques failed to establish a clear diagnosis. This makes arthroscopy an important diagnostic tool for some common anomalies around the wrist.
| Diagnostic Indications | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Ganglion | A cavity in a joint capsule filled with thick fluid |
| SL-lesion | Tear of the Scapholunate ligament |
| LT-lesion | Tear of the Lunotriquetral ligament |
| TFCC-lesion | Tear in the TFCC. Classification according Palmer Classification in traumatic or degenerative lesion |
| Synovitis | Inflammation of the synovial membrane |
| Cartilage decrease | A short of cartilage can cause arthritis |
Top of page
Summary
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive operating technique that can be used to treat or diagnose wrist problems. To perform a wrist arthroscopy the patient has to be positioned in such a way that the surgeon can use the traction apparatus and access the wrist with the instruments through the portals. Depending on the medical problem a dry or wet arthroscopy can then be performed.
Diagnostic wrist arthroscopy is eligible when a patient encounters persistent wrist pain after conservative therapy. Another possibility to carry out a diagnostic wrist arthroscopy is when other imaging techniques need confirmation on observed uncertainties or when other imaging techniques failed to establish a clear diagnosis. This makes arthroscopy an important diagnostic tool for some common anomalies around the wrist.
Several indications for performing a therapeutic wrist arthroscopy exist. The TFCC-lesion, SL-lesion, LT-lesion, the Dorsal Ganglion and the Distal radius fracture shows what the possibilities are with wrist arthroscopy.
|
Page Content |





